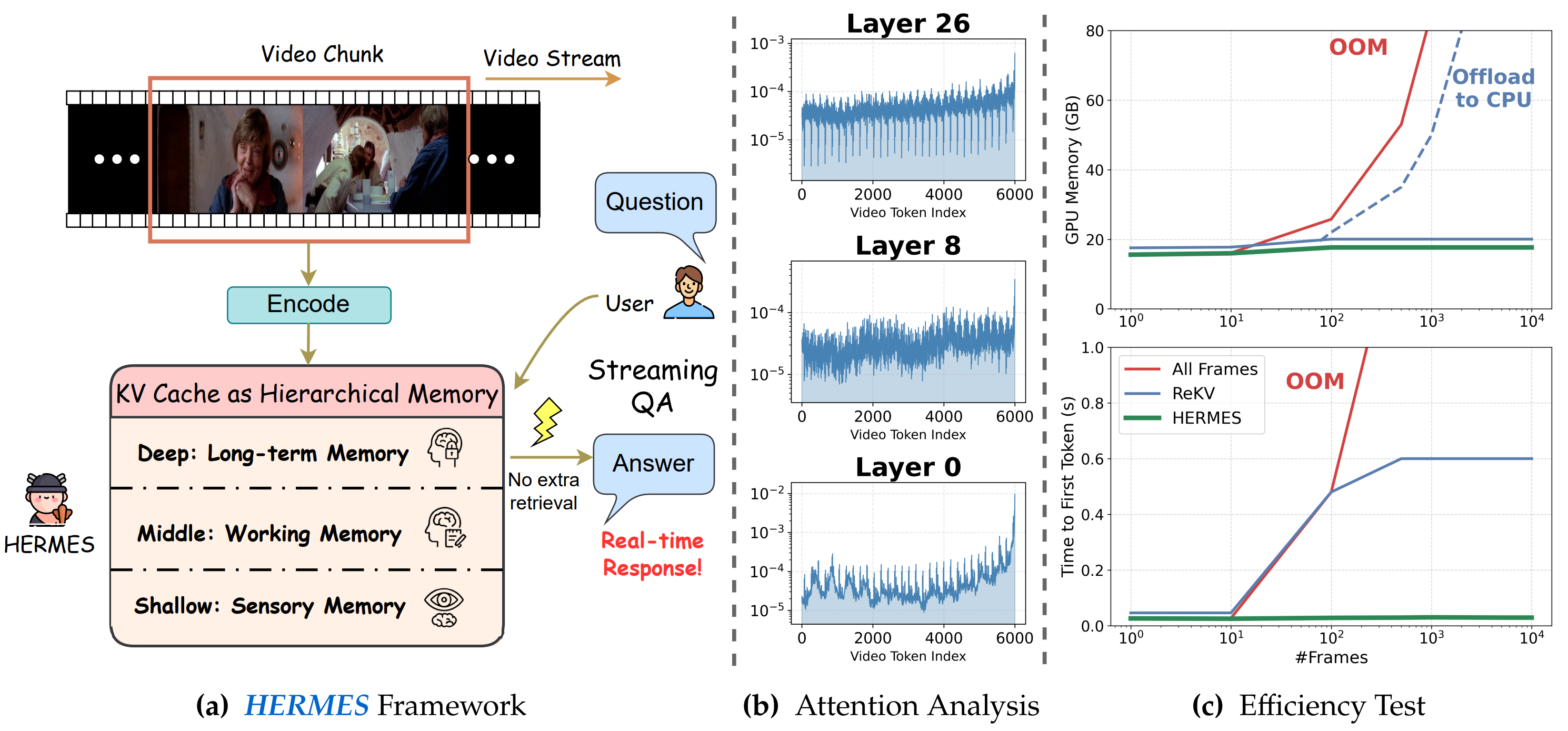
Left: HERMES is a training-free approach for efficient streaming video understanding, enabling stable inference by reusing KV cache and performing hierarchical management of video tokens stored in KV cache. Middle: HERMES is based on a mechanistic investigation of the layer-wise attention preferences over hierarchical video information. Right: We evaluate LLaVA-OV-7B on a single A800 GPU (80 GB). As input frames increase, HERMES consistently maintains extremely low latency (TTFT < 30 ms) and stable GPU memory consumption, exhibiting no risk of OOM errors and requiring no auxiliary external computational resources..
Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant improvement in offline video understanding. However, extending these capabilities to streaming video inputs, remains challenging, as existing models struggle to simultaneously maintain stable understanding performance, real-time responses, and low GPU memory overhead. To address this challenge, we propose HERMES, a novel training-free architecture for real-time and accurate understanding of video streams. Based on a mechanistic attention investigation, we conceptualize KV cache as a hierarchical memory framework that encapsulates video information across multiple granularities. During inference, HERMES reuses a compact KV cache, enabling efficient streaming understanding under resource constraints. Notably, HERMES requires no auxiliary computations upon the arrival of user queries, thereby guaranteeing real-time responses for continuous video stream interactions, which achieves 10× faster TTFT compared to prior SOTA. Even when reducing video tokens by up to 68% compared with uniform sampling, HERMES achieves superior or comparable accuracy across all benchmarks, with up to 11.4% gains on streaming datasets.
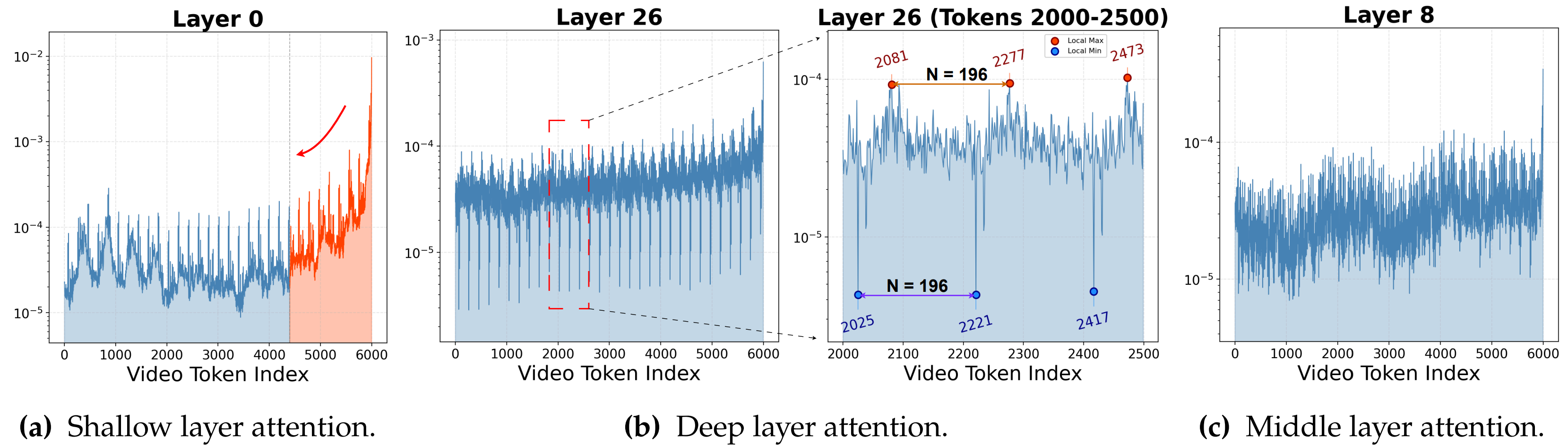
Visualization of the average attention weights (log scale) for user queries over video tokens in \llava with a FIFO KV cache budget of 6K video tokens per layer, averaged across 300 user video questions.
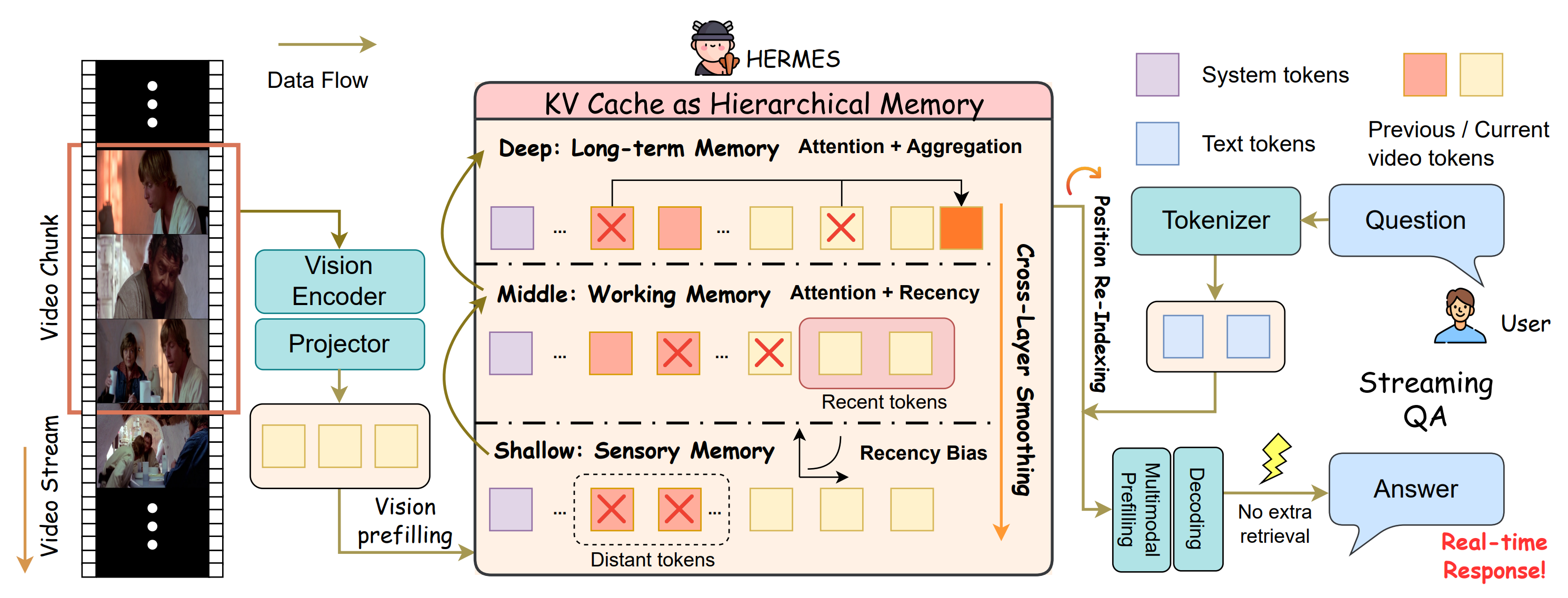
Overview of the HERMES architecture for streaming video QA. By implementing a hierarchical KV cache and specialized management strategies, HERMES enables real-time and accurate responses through direct cache reuse, eliminating the need for additional retrieval operations or external memory whenever users pose questions.
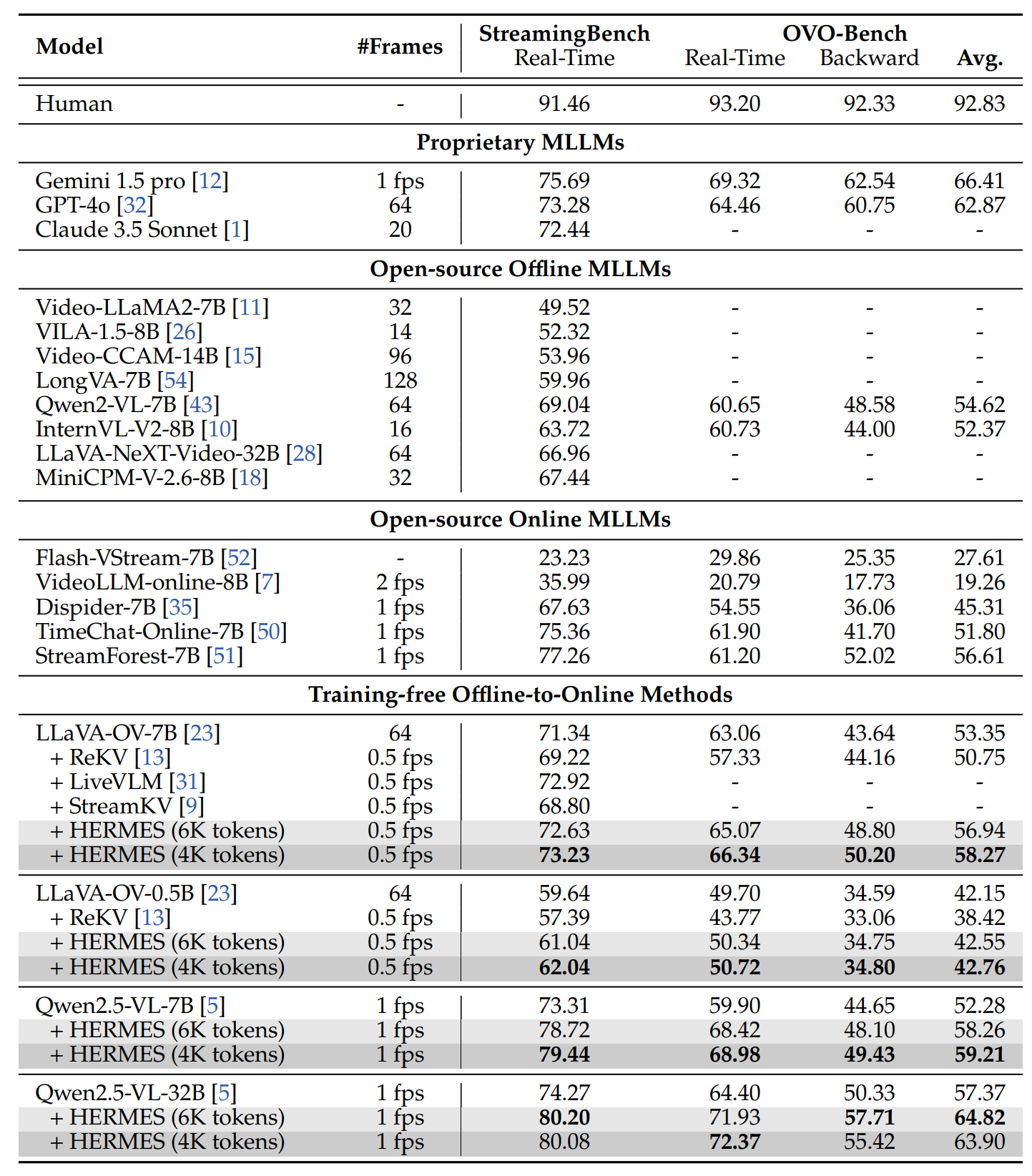
Performance comparison (%) on StreamingBench and OVO-Bench. The "Avg." column reports the results of the average accuracy of real-time visual perception and backward tracing tasks.
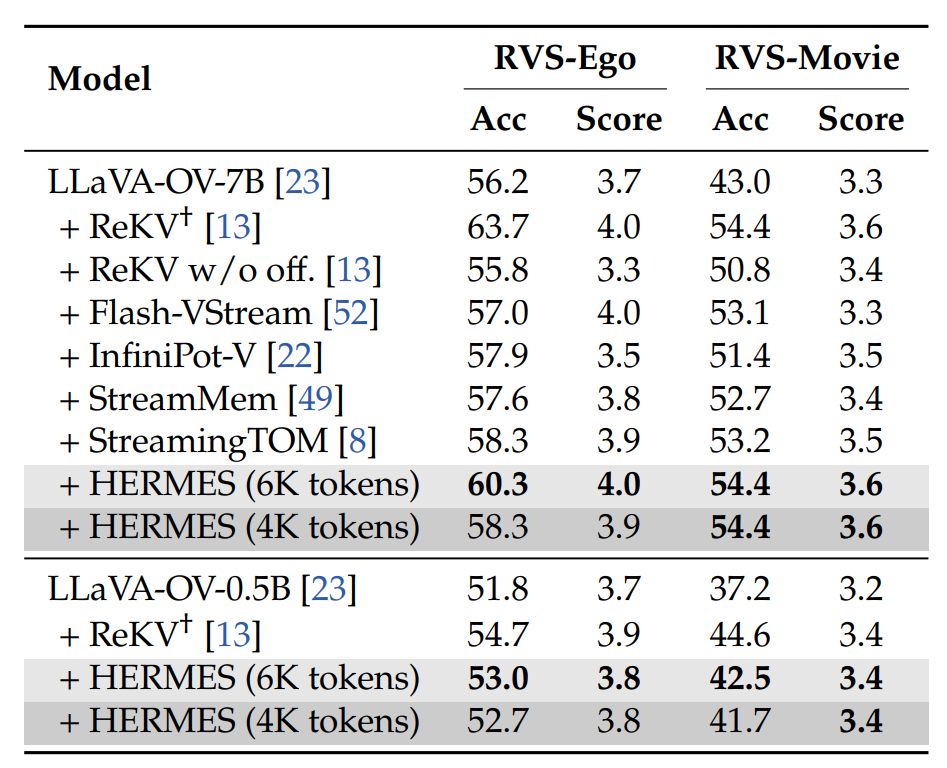
Performance on RVS-Ego and RVS-Movie. †: ReKV caches the KV states of all previously seen frames and is therefore treated as an upper bound.
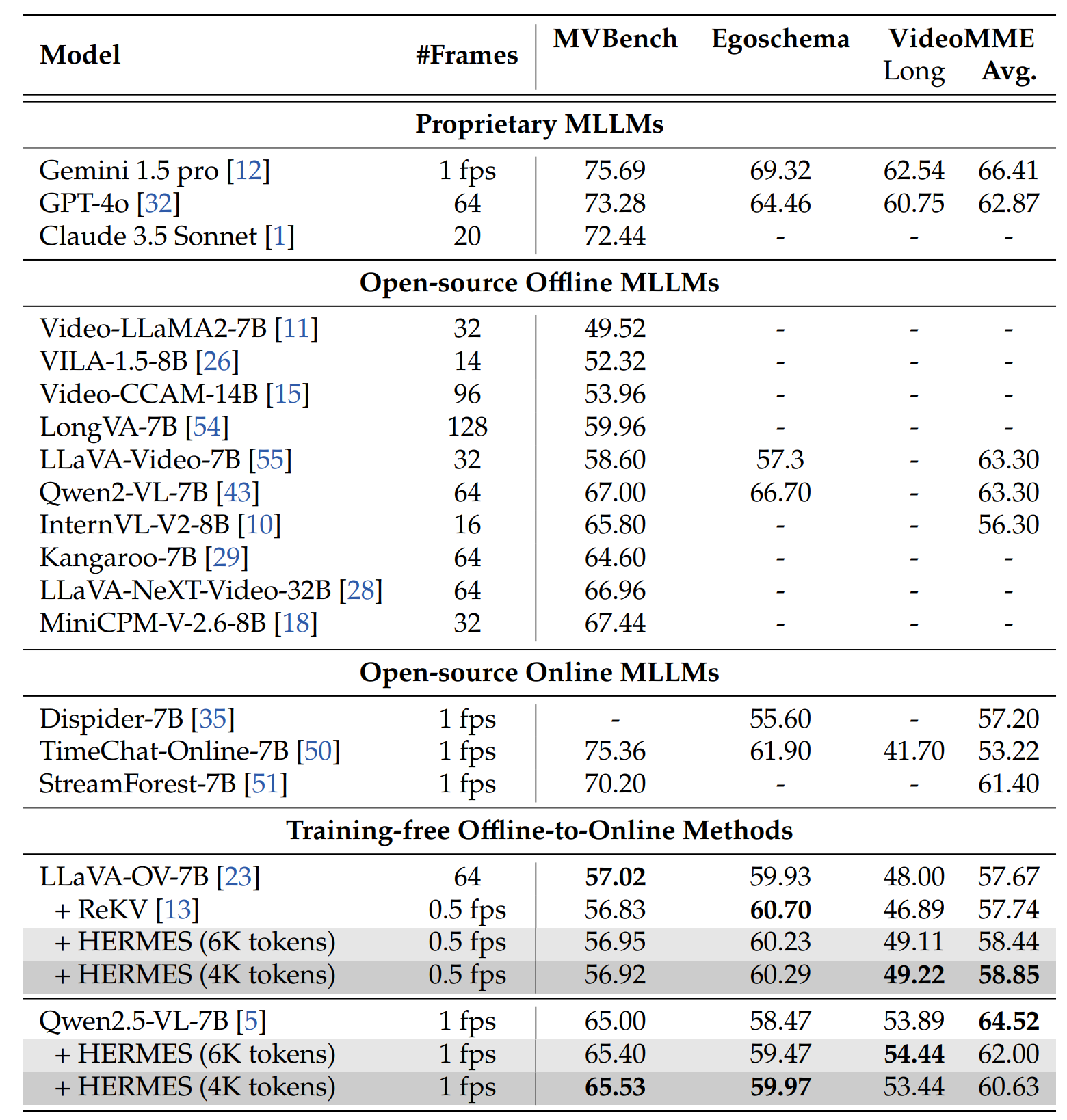
Performance comparison (%) on offline benchmarks.
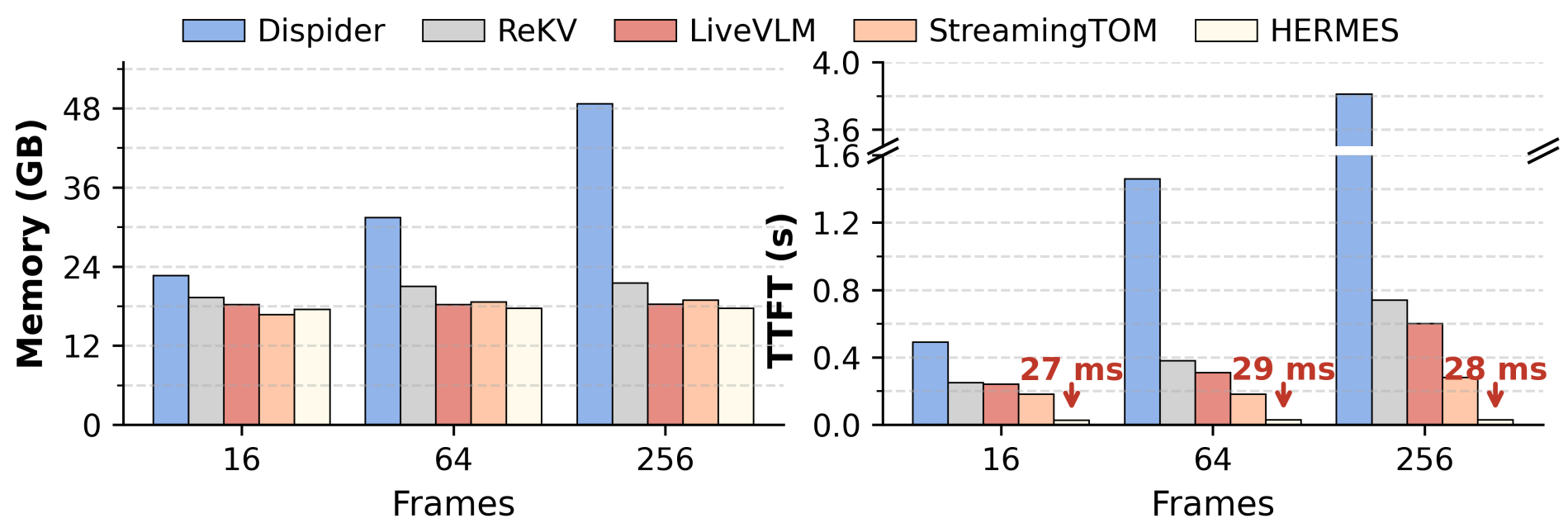
GPU memory and TTFT latency comparison across input frame numbers. HERMES achieves 10× faster in TTFT compared to prior SOTA.
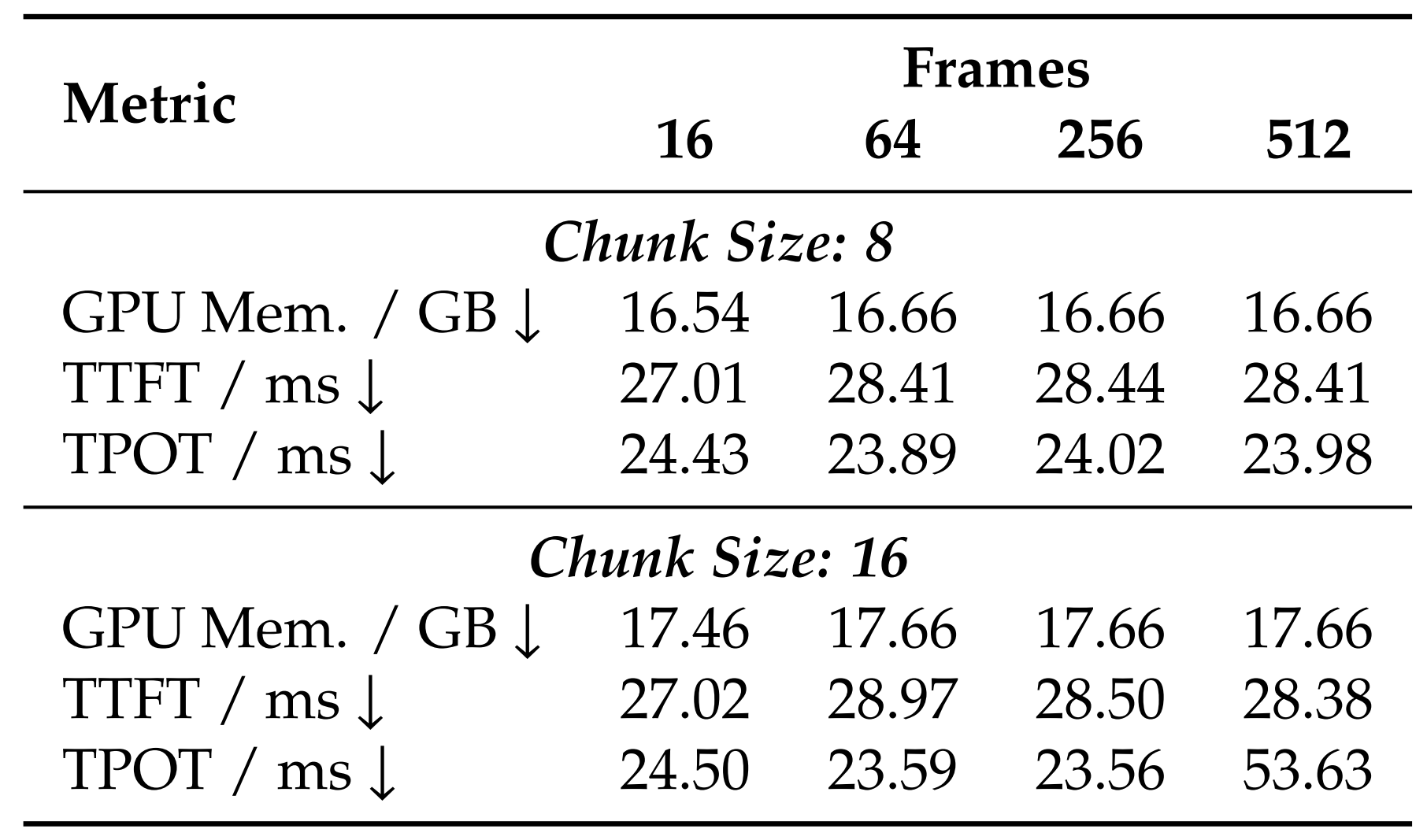
Efficiency across input frame numbers under two chunk sizes. "TTFT" denotes Time to First Token and "TPOT" denotes Time Per Output Token.
@misc{zhang2026hermeskvcachehierarchical,
title={HERMES: KV Cache as Hierarchical Memory for Efficient Streaming Video Understanding},
author={Haowei Zhang and Shudong Yang and Jinlan Fu and See-Kiong Ng and Xipeng Qiu},
year={2026},
eprint={2601.14724},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14724},
}